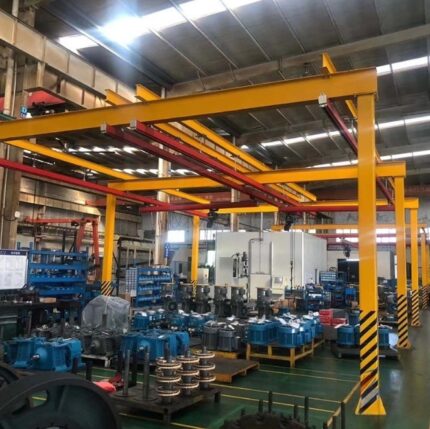
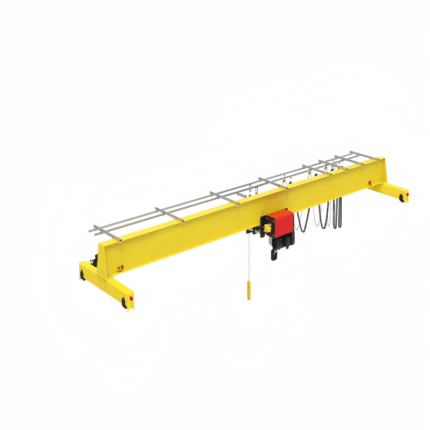
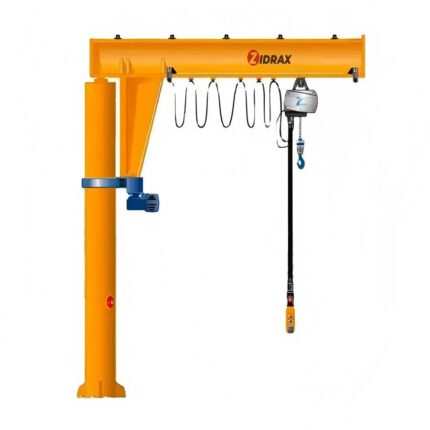
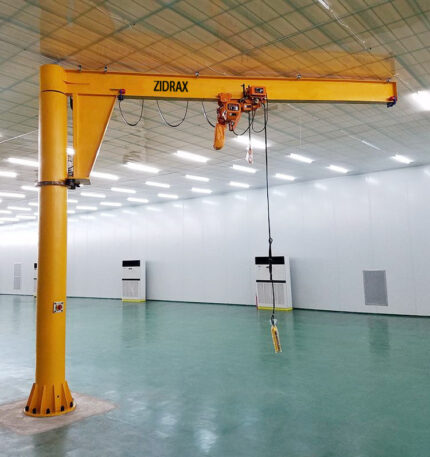
What Is a Wall Mounted Jib Crane?
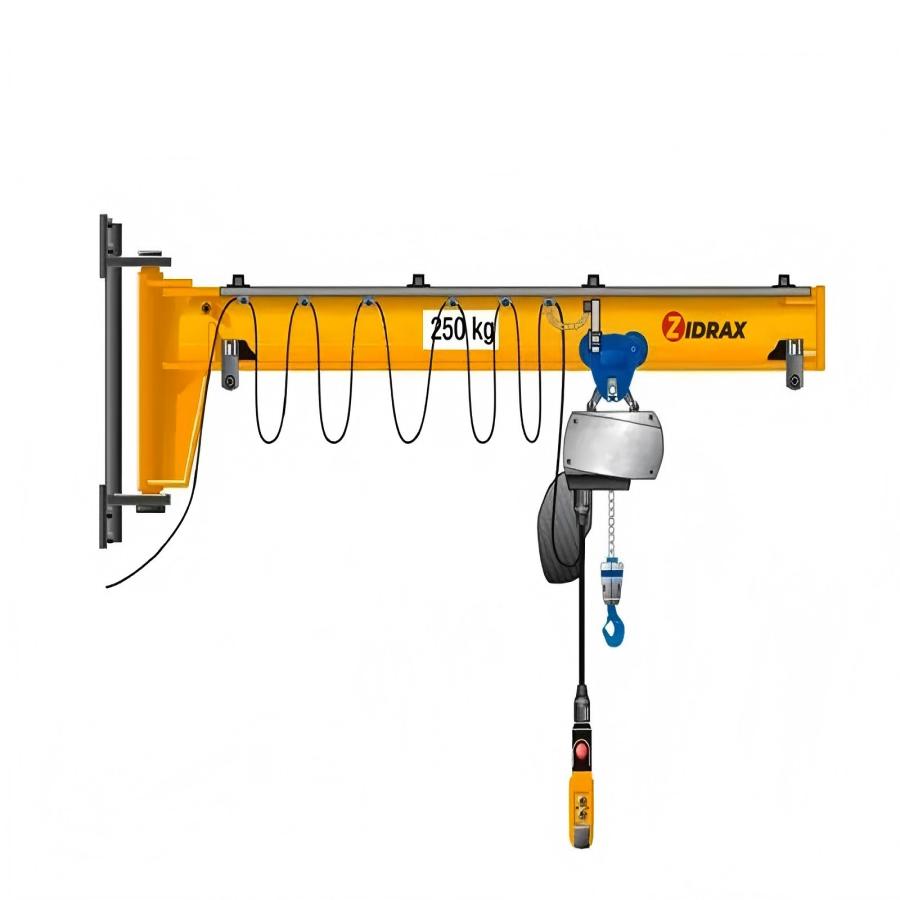
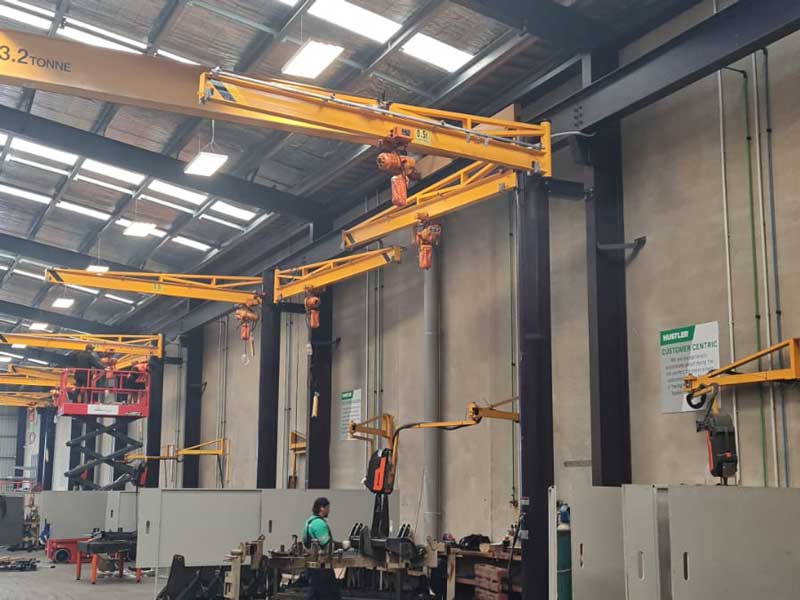
A wall mounted jib crane is a cantilevered lifting system fixed to a wall or structural column, featuring a horizontal boom that rotates horizontally to move loads within a confined arc. Unlike freestanding pillar jib cranes, wall mounted models rely on existing building structures for support, freeing up floor space and reducing installation costs.
Key Features:
Load Capacity: Typically 0.25–10 tons.
Rotation Angle: 180°–220°, depending on design.
Span: 2–10 meters (boom length).
Applications: Machinery maintenance, assembly line part transfers, small-scale material handling.
Industries: Automotive repair, manufacturing, aerospace, and packaging.
Key Components and Working Principle
Key Components:
- Boom (Jib Arm):
- Material: High-tensile steel (ASTM A36) or aluminum for lightweight models.
- Design: Box-section or I-beam for rigidity.
- Wall Bracket:
- Anchors the crane to the wall or column.
- Includes reinforcement plates to distribute load stress.
- Rotation Mechanism:
- Slewing Ring: Enables smooth rotation (manual or motorized).
- Gear-Driven: For precision control in electric models.
- Hoist System:
- Electric Chain Hoist: Common for 1–5 tons.
- Wire Rope Hoist: Suitable for heavier loads (up to 10 tons).
- Trolley:
- Moves along the boom to position loads horizontally.
- Safety Devices:
- Load limiters, rotation stops, and emergency brakes.
Working Principle:
- The crane is anchored to a load-bearing wall or column.
- The hoist lifts the load vertically, while the trolley moves it along the boom.
- The slewing ring allows the boom to rotate within a defined arc (e.g., 180°), covering the work area.
- Operators control movements via pendant, remote, or automated systems.
Comparison: Wall Mounted vs. Pillar Jib Cranes
| Feature | Wall Mounted Jib Crane | Pillar Jib Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Support Structure | Wall/column-mounted, no floor footprint | Freestanding, requires floor space |
| Rotation Range | Limited (180°–220°) | Full 360° rotation |
| Load Capacity | Up to 10 tons | Up to 20 tons |
| Installation Cost | Lower (uses existing structures) | Higher (requires foundation work) |
| Mobility | Fixed position | Portable models available |
| Best For | Space-constrained indoor facilities | Outdoor yards or large workshops |
How to Choose the Right Wall Mounted Jib Crane for Your Facility
Step 1: Assess Load Requirements
- Maximum Load: Include dynamic forces (e.g., acceleration).
- Frequency of Use: Opt for higher-duty cycles (e.g., FEM 1.001M) for intensive operations.
Step 2: Evaluate Structural Support
- Wall Strength: Concrete walls must withstand ≥4x the crane’s load.
- Column Compatibility: Steel columns should have H-beam or I-beam profiles.
Step 3: Determine Span and Rotation Angle
- Span: Match boom length to workspace dimensions.
- Rotation: 180° for linear workflows; 220° for wider coverage.
Step 4: Select Power and Control Options
- Manual Rotation: Cost-effective for light-duty use.
- Electric Rotation: Ideal for precision and heavy loads.
- Wireless Remote: Enhances operator safety and flexibility.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Installation
Mistake 1: Ignoring Wall Integrity
- Risk: Wall failure under load.
- Solution: Conduct a structural engineer’s assessment; reinforce with steel plates if needed.
Mistake 2: Incorrect Boom Alignment
- Risk: Uneven stress distribution.
- Solution: Use laser levels to ensure horizontal alignment.
Mistake 3: Overlooking Rotation Clearance
- Risk: Boom colliding with equipment.
- Solution: Map rotation paths and maintain ≥0.5m clearance.
Mistake 4: Skipping Load Testing
- Risk: Undetected mechanical flaws.
- Solution: Perform 125% SWL static and dynamic tests post-installation.
Understanding Rotation Angles in Wall Jib Cranes
Rotation angle is a critical factor in the performance and suitability of wall jib cranes. It refers to the horizontal range that the jib arm can sweep while pivoting around its mounting point. Most wall mounted jib cranes offer rotation angles ranging from 180° to 220°, depending on their structural design and installation conditions.
A 180° rotation is standard for wall-mounted models, allowing the crane to cover a semi-circular area directly adjacent to the wall. This setup is ideal for workstations, loading docks, or along production lines where lateral movement is required within a defined area. In some configurations, 220° rotation can be achieved by optimizing the mounting and arm clearance, providing slightly broader coverage.
The choice of rotation angle directly affects the crane’s working envelope and flexibility. A wider angle offers greater access and coverage, reducing the need for repositioning or multiple units. However, the actual achievable angle may be restricted by surrounding obstructions like walls, columns, or machinery.
Selecting the appropriate rotation angle is essential to maximize operational efficiency while ensuring safe and smooth crane operation. Proper planning during installation ensures the crane can fully utilize its design capabilities without interference or performance loss.
Enhancing Productivity with Ergonomic Wall Jib Crane Solutions
A. Ergonomic Controls
- Anti-Fatigue Pendants: Lightweight, intuitive interfaces reduce operator strain.
- Variable Speed Settings: Precision handling for fragile loads.
B. Automation Integration
- PLC Systems: Sync crane movements with conveyor belts or robotic arms.
- Position Sensors: Auto-stop at predefined locations to streamline workflows.
C. Modular Attachments
- Quick-Change Tools: Swap hooks, magnets, or grabs in seconds.
- Tool Balancers: Counteract load weight, minimizing manual effort.
D. Space Optimization
- Foldable Booms: Retract when not in use to clear aisles.
- Ceiling-Mounted Tracks: Combine with wall cranes for 3D material flow.
For inquiry, please send email: info@zidraxcranes.com